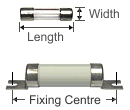
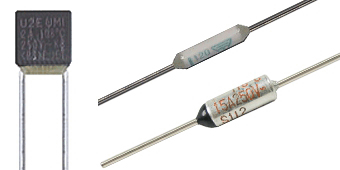
A thermal fuse or thermal cutoff is a safety device which open circuits against overheat. It detects the heat caused by the over-current due to short circuit or component breakdown. Thermal fuses do not reset themselves when the temperature drops like a circuit breaker would. A thermal fuse must be replaced when it fails or is triggered.
Unlike electrical fuses or circuit breakers, thermal fuses only react to excessive temperature, not excessive current, unless the excessive current is sufficient to cause the thermal fuse itself to heat up to the trigger temperature.
What is a Thermal Fuse?
What’s the purpose of a thermal fuse?
The purpose of a Thermal fuse is typically to be a cutoff for heat producing devices. As the name implies, thermal fuses are usually found in heat-producing electrical appliances such as coffee makers and hair dryers. They function as safety devices to disconnect the current to the heating element in case of a malfunction (such as a defective thermostat) that would otherwise allow the temperature to rise to dangerous levels, possibly starting a fire.
How to tell if a thermal fuse has blown?
To test if your thermal fuse has blown, touch the right side of your multimeter lead to the right side of the fuse, and repeat with the left multimeter lead. If the multimeter needle fails to move, this indicates the thermal fuse has blown. Learn about testing for a blown fuse.
Depending on the appliance, if you don’t have a multimeter, you may sometimes be able to tell if a thermal fuse has blown. For example, if the applicance is a dryer and it is operating, but not heating, it is probably a blown fuse designed to protect the heating element.
Depending on the appliance, if you don’t have a multimeter, you may sometimes be able to tell if a thermal fuse has blown. For example, if the applicance is a dryer and it is operating, but not heating, it is probably a blown fuse designed to protect the heating element.
Elcut Thermal Fuse Terminology.
The following definitions apply to our range of Elcut thermal fuses:
Opening Temperature / Cut-off Temperature
The temperature at which the thermal fuse opens (fuses off) while passing 0.1 amp or less in a controlled oil bath at arise of 1 C per minute. The functioning temperature is not the Rated Functioning Temperature.
Rated Functioning Temperature (Tf)
Rating of the functioning temperature based on safety standards. Tolerance of rated functioning temperature is +0, -10 C for IEC 60691. Tolerance for METI is ±7 C except some types.
Holding Temperature (Th)
The highest temperature of the thermal fuse at which it does not open the circuit while passing rated current for 168 hours. (Applicable to UL, cUL and CCC).
Maximum Temperature Limit (Tm)
The highest temperature of the thermal fuse at which continuity does not occur for 10 minutes after the function of the thermal fuse.
Maximum Use Temperature
The highest temperature of the thermal fuse at which it does not function or the functioning temperature does not become higher remarkably after being exposed for a certain amount of time.
Rated Current (Ir)
The allowable maximum current which the thermal fuse is able to carry.
Rated Voltage (Ur or Vr)
The allowable maximum voltage which can be applied to the thermal fuse.
Shop our range of Thermal Fuses.
We stock a range of PCB mount thermal fuses in both axial and radial lead types.
Opening Temperature / Cut-off Temperature
The temperature at which the thermal fuse opens (fuses off) while passing 0.1 amp or less in a controlled oil bath at arise of 1 C per minute. The functioning temperature is not the Rated Functioning Temperature.
Rated Functioning Temperature (Tf)
Rating of the functioning temperature based on safety standards. Tolerance of rated functioning temperature is +0, -10 C for IEC 60691. Tolerance for METI is ±7 C except some types.
Holding Temperature (Th)
The highest temperature of the thermal fuse at which it does not open the circuit while passing rated current for 168 hours. (Applicable to UL, cUL and CCC).
Maximum Temperature Limit (Tm)
The highest temperature of the thermal fuse at which continuity does not occur for 10 minutes after the function of the thermal fuse.
Maximum Use Temperature
The highest temperature of the thermal fuse at which it does not function or the functioning temperature does not become higher remarkably after being exposed for a certain amount of time.
Rated Current (Ir)
The allowable maximum current which the thermal fuse is able to carry.
Rated Voltage (Ur or Vr)
The allowable maximum voltage which can be applied to the thermal fuse.
Shop our range of Thermal Fuses.
We stock a range of PCB mount thermal fuses in both axial and radial lead types.